TL; DR
While LLMs like ChatGPT are reshaping how people access information, they won’t replace Google anytime soon. Instead, they’re creating new visibility channels beyond traditional rankings. For SEO, this shift means adapting strategies to optimise for both search engines and language models by prioritising helpful, structured, and cited content.
There’s no limit to what an efficient large language model can do today!
Adopting these powerhouse tools in workplaces has been surprisingly faster, pushing their estimated market size to USD 75.5 Bn by 2034.
From a digital marketing lens, LLMs are used for SEO and content creation, from brainstorming ideas, creating drafts, optimising for SEO, checking for grammar errors, and generating images.
They are the right tool to feature your content on Gen AI engines, like Google AI Overviews.
The other side of the lens shows that millions of users are ditching Google and turning more to generative engines for their preliminary search.
Does this mean Google’s monopoly over organic search has finally ended?
What does this transition mean for businesses seeking organic search traffic from conventional SEO methods?
Before answering these questions, let’s examine LLMs and their relationship with content, research, and SEO more closely.
The Altering Search Pattern in the Gen AI Era (and Its Impact on SEO)
Generative AI models (LLMs) have indeed transformed how people interact with search engines today. Search is no longer just about typing keywords. It is more about meaning, context, and intent. The keywords have been replaced with conversational queries and predictive personalisation.
Here are the key takeaways:
1. Search is Now More Personal than Ever
Today’s search engines, powered by AI, adapt to your preferences, device usage, and browsing history. Answers to search queries are tailored accordingly, sometimes before you even realise what you need.
2. Intent > Keywords (Semantic Search)
The rigid keyword-stuffing era is now history. LLM-driven search can now decode the real intent and sentiment behind user queries (including conversational phrases). These search engines can match every nuance with precision.
3. Search Goes Conversational with LLMs
The line between search engines and chatbots is blurring. Platforms like LLMs allow users to ask complex, natural-language questions. In return, coherent, summarised answers are generated, not just blue links. The altered search patterns will impact the search engine optimisation strategy.
Key Takeaway: SEO professionals must dig deep to analyse user intent and behaviors, predict emerging trends, generate semantically rich content, improve content clusters for better discoverability, and more.
Understanding the LLM-Effect on Canonical Answers for SEO
In SEO, a canonical answer refers to the most authoritative, consistent response to a query sourced from trusted web pages. Google’s algorithm selects this based on structured data, relevance, and backlinks.
This was from a traditional search engine perspective.
Comparatively, generative models like ChatGPT or Gemini don’t retrieve; they generate. These generative AI models use learned patterns, not real-time facts, and often paraphrase instead of linking back.
What does it mean for businesses?
Even if websites are at the top of their SEO game, there’s no guarantee that their websites will appear on top of SERPs. LLM SEO optimisation can improve how models interpret your content. But they are not reliable replacements for canonical clarity. Professionals should develop a different mindset regarding website SEO for LLMs, which is focused on structuring content so it is referenced, not replaced.
Are LLMs a Reliable Source for Content Research in SEO?
Can AIO and other LLM tools be trusted blindly? This doubt, however, didn’t deter major players from investing aggressively in generative AI.
Big Tech envisions an AI-dominated future and is expected to invest a cumulative USD 325 billion in infrastructure development by 2025. The investment is deemed a progressive approach towards converting a large language model (LLM) into a perfect intelligent assistant. Unfortunately, the flaws are hard to ignore!
Hallucination, bias, misinformation, privacy concerns, and copyright infringement are a few examples.
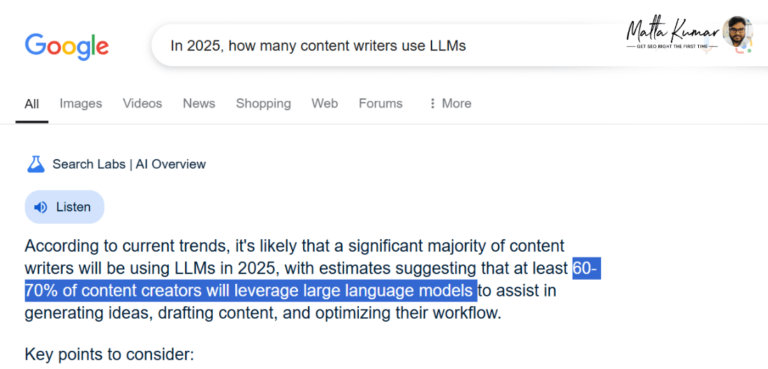
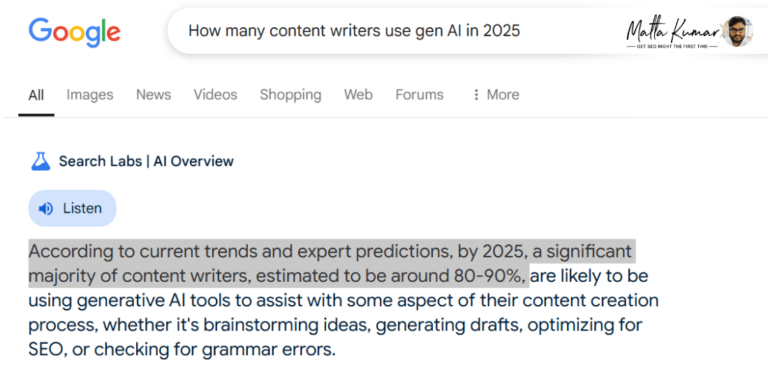
The following screenshots show two responses to the same search query on Google AI Overviews. See the discrepancies in the two search results –
First Example Screenshot
AI Overview generates two different statistics for the same query, with a subtle change in the vector placements. Also, no sources/links are attached next to the answers. These two are plausible situations of AI hallucinating because a different result was generated when the Incognito Mode was used:
Unarguably, generative engines, or LLMs, need to make a massive number of improvements before they can truly be trusted for content research.
This means traditional search engines, like Google and Bing, are still irreplaceable.
But where does this put businesses from a search engine optimisation perspective?
Since Google prioritises helpful, relevant, and quality content, LLMs can be used for SEO optimisation through content that closely resembles the user intent behind every search query and is curated more for conversational searches.
With appropriate content and the right on-page SEO tactics, your website will gain more visibility, for example, appearing frequently on Google AI Overview summaries.
That said, information reliability remains largely unaddressed.
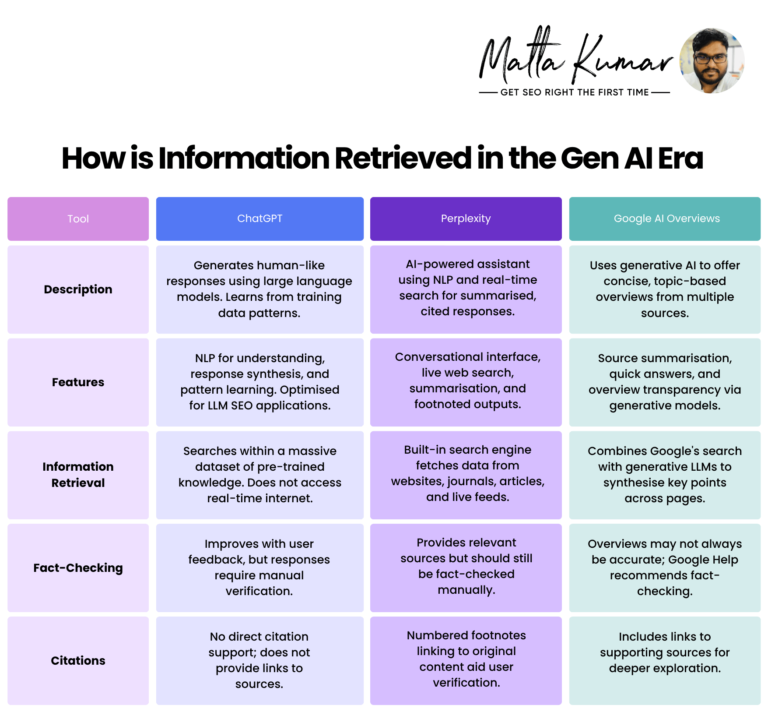
How is Information Retrieved in the Gen AI Era
Large Language Models, or LLMs, like ChatGPT and Perplexity, are slowly crawling into every writer, SEO professional, and designer’s laptop.
This is a new trend.
But their information retrieval methods are questionable.
A comparative overview of the tools and their methods is presented below:
Why LLMs Concern Individual Publishers?
Large Language Models (LLMs) are changing how users engage with content online. From instant summaries to in-depth generative answers, platforms powered by LLMs are now central to the search experience.
High-authority websites continue to benefit, appearing in AI overviews and earning citations.
However, individual publishers face a tougher battle.
Niche sites are losing visibility due to “zero-click” searches, where users get the answer without clicking through. With dwindling traffic and fewer monetisation opportunities, many independent creators are stepping back, thus risking the future of unique, quality content.
How can Publishers Adapt to the Zero-Click Era?
LLM-powered SEO has reshaped the search landscape. Therefore, publishers can no longer rely solely on traditional traffic funnels. The zero-click era demands a shift in both mindset and strategy.
Here’s how the ecosystem can evolve:
Rethink Visibility, Not Just Ranking
With LLMs in SEO becoming the norm, it’s no longer just about being ranked—it’s about being referenced. LLM SEO optimisation means ensuring your content is structured, semantically rich, and easily extractable by AI systems for inclusion in responses.
Invest in SEO Custom LLMs
Some publishers are exploring SEO custom LLMs that are tailored language models trained on niche datasets to retain content control and create proprietary search experiences. This hybrid approach can keep users engaged within a publisher’s ecosystem.
LLM Optimisation Is the New On-Page SEO
Traditional on-page SEO now needs to co-exist with LLMO (LLM Optimisation). Structuring content for AI readability, adding contextual metadata, and adopting schema markup can help improve how LLMs interpret and surface your content.
Monetisation Models Must Evolve
Since LLMs in SEO often bypass traditional click-through paths, publishers must pivot to monetisation strategies such as direct subscriptions, AI-generated newsletter digests, and affiliate models built into the AI experience.
Collaborate with Ad Tech Innovators
Ad networks and platforms are experimenting with new ad formats designed for generative environments. These include embedded sponsored snippets within LLM outputs. They open a new path for visibility and revenue.
Other Limitations of Gen AI Search Engines
Gen AI has reshaped search. But it is far from perfect. Using LLMs for content and SEO will help brands get featured more on conversational, intent-driven results. Yet, there are still significant roadblocks.
No Real-Time Data Access
Unlike traditional search engines, most LLMs don’t access live web content.
They rely on static training data, which means their answers may be outdated or irrelevant to fast-changing topics like news, finance, or product updates.
Struggles with Nuance and Context
They may misinterpret sarcasm, cultural references, or industry-specific terminology despite being trained on massive datasets.
Inaccurate or Fabricated Citations
One major flaw is citation accuracy. Gen AI models often “hallucinate” sources, thus presenting incorrect or non-existent references as fact.
Poor Source Verification
LLMs don’t always evaluate the credibility of their information. They may pull details from forums, outdated pages, or low-authority sites without discrimination.
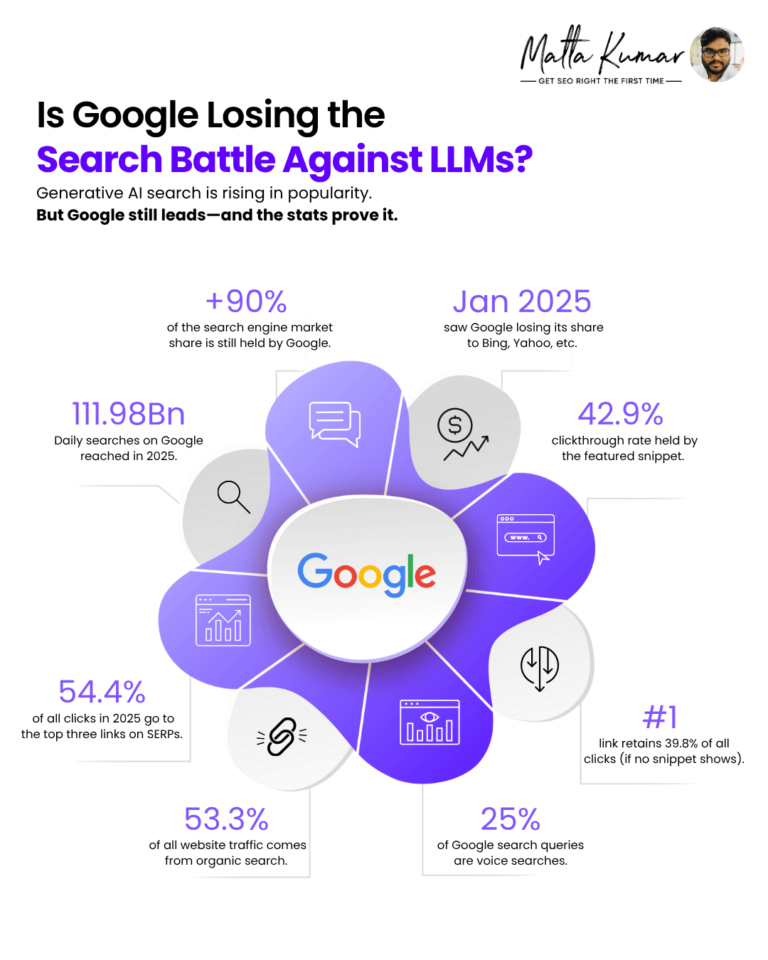
Is Google Losing the Search Battle Against LLMs?
- 1. Daily searches on Google reached 111.98 Bn in 2025.
- 2. Google's global search engine market share remains consistently above 90%.
- 3. However, the search engine giant lost a chunk of its share to other traditional search engines (Bing, Yahoo, DuckDuckGo, and others) in January 2025.
- 4. The featured snippet on the SERP has a 42.9% clickthrough rate (CTR).
- 5. The #1 link in the organic search result gets 39.8% of all clicks (if a featured snippet is absent).
- 6. In 2025, the top three links on Google search results still get 54.4% of all clicks.
- 7. Nearly 53.3% of all website traffic this year comes from organic search.
The data implies that LLMs are replacing neither organic search nor Google. While Google did lose some market share to the second and third-best players, its position as the unchallenged leader of organic search remains intact.
From this data snapshot, the inference is that organic search will continue, and so will SEO’s undeniable role. The only change is how the two entities will coexist with the generative AI models because their presence can not be ignored for long.
Let’s find out how search engine optimisation will function in an era of coexistence between organic and LLM search engines.
The Importance of SEO in Digital Marketing - A Brief Overview
Search engine optimisation (SEO) is the cornerstone of digital marketing. From driving visibility to organic traffic, building site credibility to digital marketing effectiveness, SEO shoulders the heavy lifting single-handedly.
In the generative AI era, SEO’s role has transitioned to enhancing websites’ relevance for users’ search intent. Its responsibility has extended beyond the keyword-matching threshold to bringing more relevant information to the front that closely aligns with exactly what users want, need, and desire.
Since Google is still leading the search game on a global front, traditional SEO best practices are still acceptable; however, with a slight twist to attune to the search algorithms of generative AI engines.
An alternative to SEO is GEO. Also termed as generative engine optimisation, GEO functions similarly to SEO but follows the LLM algorithms.
Having said that, SEO professionals are opting for a common approach, which is a blend of both GEO and SEO to get better results that equally harness the power of traditional and gen AI models.
The Correlation Between SEO and LLMs/AI Overviews
Google AI Overviews and other Large Language Models (LLMs) have already started dominating the SERP experience.
This means SEO has to undergo a paradigm shift to ensure your website content is easily identified, consumed, and trusted.
As stated earlier, SEO for LLMs and AI Overviews is comparatively different from how it was (or is) done for traditional searches.
The impact is both positive and negative.
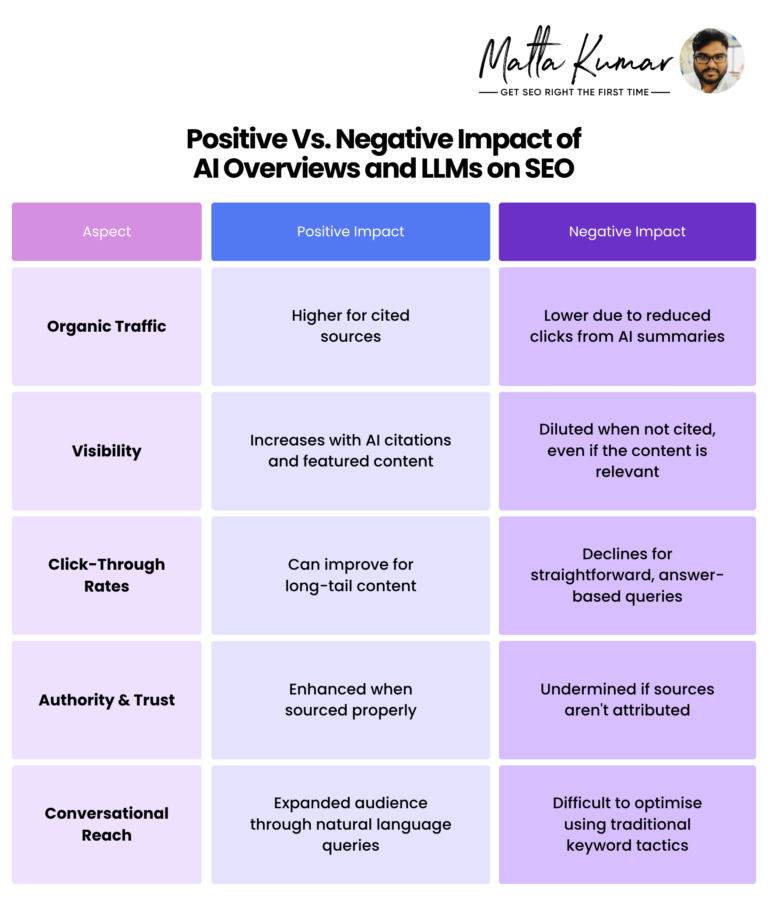
Positive Vs. Negative Impact of AI Overviews and LLMs on SEO
AI Overviews and LLMs are challenging SEO professionals to rethink their strategies for better visibility on conversational answer summaries. The former has impacted the search game and altered the rules. SEO optimisation for LLMs is not much different, comparatively. However, LLMs do have a few negative impacts, especially for websites that were performing well under the traditional search rules.
However, if you examine how AI overviews generate results for search queries more closely, you will detect a similar pattern to that of traditional search engines.
For instance, the approach to appearing as citations on AI Overviews’ summaries is identical to how website links appeared in the top three positions of SERPs (traditional search). The similarity lies in that Google AI overviews and other LLMs pull content directly from web sources.
What does this mean for SEO?
Using the best SEO practices, you can get your website cited in featured answers. For example, build your content to be informative, present it in a structured way, and mark it up using schema.
This will help drive authoritative visibility to your content. Google advises publishers to follow its guidelines and enable structured data for inclusion in Google Search results.
That said, individual publishers are still worried because of low click-through rates. The ‘zero-click’ approach, as mentioned earlier, has resulted in a 34.5% drop in position 1 CTR, especially where AI Overviews were present on SERPs.
A reduction in organic traffic and click-throughs can be damaging for top-funnel content. This means that LLM SEO optimisation may bring visibility to your website, not visitors. Additionally, ranking uncertainty is a concern, as traditional SEO signals like backlinks and on-page optimisation carry less weight in LLM SEO environments. LLMs are reshaping ranking logic, making it harder to track what’s working.
These are two negative impact examples of generative AI search engines on SEO.
Here’s a comparative analysis of the positive and negative impacts:
AI Overviews/LLMs are Not a Replacement for Google and SEO - Here’s Why?
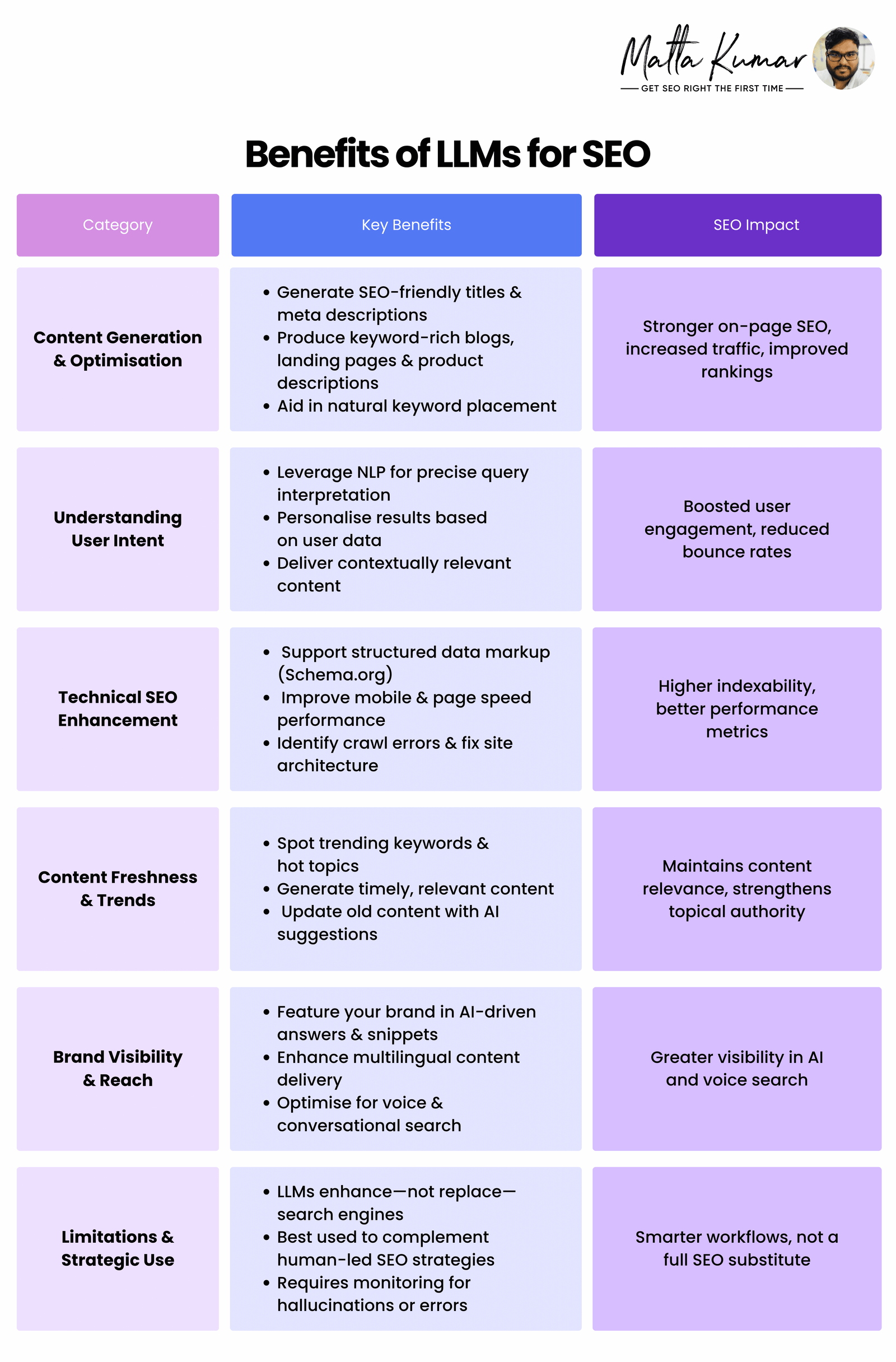
LLM tools can be used to optimise your website content further, unlock scalable, search-friendly content strategies, and future-proof your digital presence. And just like that, your website SEO will improve and generate better results.
Here’s a summary of how LLM tools can truly benefit your SEO strategy:
Benefits of LLMs for SEO
SEO ranking in ChatGPT is great, but how do you know it is even working? With proper tracking tools, you can affirm visibility in ChatGPT. This is now a vital part of your SEO analytics. While AI-driven traffic is harder to quantify, there are emerging ways to trace mentions, visibility, and indirect traffic from the LLM.
This is how you can measure your SEO strategy for ChatGPT:
AI Crawlers Are Rewriting the Rules - What Does it Mean for SEO
Despite Google’s dominance over search engines, the online market remains volatile because of seismic changes being triggered by generative AI. The traditional search might not drift into oblivion completely; however, its #1 position is under threat. AI Overviews and other LLM platforms are catching up faster than you blink. That truly means your legacy SEO approaches need a dramatic revamp. One of the main reasons behind this is that LLM Bots are crawling the web at record speed.
According to data, AI bots now account for 18.9% of all bot traffic, closing in on traditional search engine bots’ 34.6% (primarily Google bots). In just the past few months, LLM crawlers like GPTBot, ClaudeBot, and PerplexityBot have grown so rapidly that AI bot activity now represents nearly a quarter of all crawler traffic online.
And the scary part is that they aren’t slowing down. The number of AI crawlers has doubled since late 2023, with 21+ major LLM bots actively indexing the web.
In simple terms, AI search engines aren’t experimenting. They’re establishing dominance speedily. You’re missing the bigger picture if you’re still optimising only for Google’s legacy crawlers.
To understand how this change will impact SEO, here are a few points to consider:
- Traditional search rankings are no longer the only visibility that matters.
- Your content must be optimised for LLM comprehension, not just Google’s algorithm.
- Blocking or ignoring AI crawlers can limit your content’s exposure across new AI-driven platforms.
This only means that now your website content must show up at:
- ChatGPT
- Claude
- Perplexity
- Gemini
- Google Search’s AI Overviews
Key Takeaway: AI bots are crawling faster, and users are shifting their queries to conversational AI. Therefore, today’s SEO success requires visibility across traditional SERPs and AI-driven answer engines.
Your traffic forecasts are already outdated if your SEO playbook doesn’t include AI search optimisation.
Conclusion
With the rise of LLM SEO, many wonder if LLMs will replace Google. The answer is no.
While large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT are changing how users interact with content, they are not search engines. Instead, they complement SEO by enhancing content creation, improving keyword optimisation, and offering deeper insights into user intent.
For SEOs, the future lies in combining traditional search strategies with LLM-powered tools, meaning adapting to change without abandoning core SEO principles.